Uncategorized
The “heart” of the car: the basic structure of the engine introduction
The automobile engine is the car’s “soul,” determining its power, economy, stability, and environmental impact. It is a complex system, but the basic principles are the same for all cars. Let’s explore the car engine to understand how it works and how to protect it for a longer lifespan.
The role of the automobile engine
An automobile engine converts gasoline’s heat energy into mechanical energy by expanding combustion gas to push the piston. Automobile engines are classified into various types based on different factors:
- Intake system: naturally aspirated, turbocharged, mechanically supercharged, and double supercharged.
- Piston movement: reciprocating piston or rotary piston.
- Number of cylinders: single-cylinder or multi-cylinder.
- Cooling method: water-cooled or air-cooled.
- Number of strokes: four-stroke or two-stroke internal combustion engines.
The engine is crucial as the power source of the automobile.
In addition to providing power, the automobile engine has many other important functions.
First, the automobile engine can control and regulate the operation of the automobile, including acceleration, deceleration, stopping, and other operations. Second, the car engine can affect the performance of the car, such as acceleration, top speed, and fuel economy. In addition, the engine can affect the emissions of the automobile, such as the emissions of carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. The design and manufacturing level of the engine also directly affects the reliability and durability of the automobile.
The car engine is the core component that greatly affects a car’s performance and reliability. Understanding the different engine types and how to choose and maintain them helps us better grasp how cars work, care for the powertrain, and extend the car’s lifespan.
Principles and processes of automobile engine
A gasoline engine typically consists of the crank linkage, gas distribution mechanism, and five systems: fuel supply, lubrication, cooling, ignition, and starting. A diesel engine has two main mechanisms and four systems, excluding the ignition system.
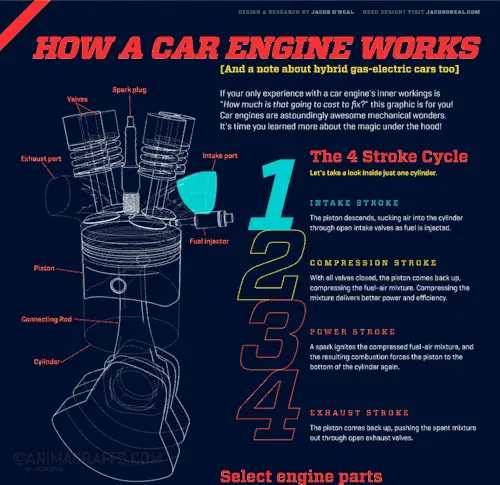
The working principle of an automobile engine involves converting thermal energy into mechanical energy through four processes: intake, compression, power (work), and exhaust. In the intake process, the air-fuel mixture enters the cylinder. During compression, the mixture is compressed. The power stroke ignites the mixture, causing an explosion that pushes the piston down. The exhaust stroke expels the combustion gases from the cylinder. These four processes make up one work cycle.
Engines use two types of duty cycles: four-stroke and two-stroke. In a four-stroke engine, the crankshaft rotates twice, and the piston moves four times to complete one cycle. In a two-stroke engine, the crankshaft rotates once, and the piston moves twice to complete one cycle.
Today, most automobiles use four-stroke engines, especially in traditional internal combustion vehicles, due to their fuel efficiency, reliability, and durability. Four-stroke, water-cooled, in-line or V-type reciprocating engines are common in modern cars.
Image source: Animagraffs https://www.facebook.com/watch/?v=1642139559216002
The principle of operation of a two-stroke gasoline engine can be briefly summarized in three stages: the first stroke, the second stroke, and the gas exchange process.
In the first stroke, the piston moves upward from the lower stop. The engine closes the three air holes, opens the intake ports, and lets the combustible mixture flow into the crankcase.As the piston moves upward, it compresses the mixture and prepares it for the subsequent combustion process.
In the second stroke, the spark plug ignites the mixture, causing the gas to expand and push the piston down. At the same time, the engine closes the intake port and compresses the mixture in the crankcase for the next gas exchange. As the piston approaches the lower stop, it opens the exhaust port and expels the exhaust gases. Next, the gas change orifice opens and the pre-compressed combustible mixture rushes into the cylinder, discharging the exhaust gases.
The gas exchange process is the heart of the work of a two-stroke engine, and it provides an important power base for the engine.
Principle of engine crank connecting rod mechanism
The crankshaft connecting rod set is a key engine component that converts the gas force from the piston and connecting rod into torque, driving the car’s transmission, gas distribution mechanism, and other auxiliary devices. The crankshaft experiences bending and torsional alternating loads from the combined effects of varying gas forces, inertia, and moments.
The role of the engine crank connecting rod mechanism is very important, and its main functions are as follows:
1. Realize the work cycle, and complete the transmission mechanism of energy conversion. The crank connecting rod mechanism plays a key role in the engine by converting the thermal energy produced by fuel combustion into mechanical energy which then drives the engine to operate normally.
2. Transmission of power mechanism. The crank linkage mechanism can transfer the power generated by the engine to the transmission system of the car, so as to realize the movement of the vehicle.
3. Determine the performance and efficiency of the engine. The structure of the crank connecting rod mechanism directly affects the performance and efficiency of the engine, so its design and manufacture need very strict standards.
Principle of Automobile Engine Gassing Mechanism
The gas distribution mechanism opens and closes the inlet and exhaust valves at regular intervals, allowing the air-fuel mixture into the cylinder and expelling exhaust gases.
The crankshaft drives the camshaft via the timing gear, moving the rocker arms through the tappet and push rod. As the cam apex passes the tappet, the valve closes under spring pressure.
The gas distribution mechanism has two parts: the valve transmission and valve groups, including components like timing gears, tappet, push rod, rocker arm, valves, valve guides, springs, oil seals, and valve seats. The working principle of the gas distribution mechanism is determined by the engine’s work cycle and ignition sequence in each cylinder.
During the compression and work stroke, closing the valves ensures the sealing of the combustion chamber. Therefore, the working principle of the gas distribution mechanism is by the requirements of the work cycle and ignition sequence in each cylinder of the engine, timed to open and close the cylinder intake and exhaust valves to ensure normal engine operation.
As a car engine, there are many types on the market, but the principles are all similar, in the next article we will continue to reveal the secrets of the car engine, so you can have a better understanding of your car. If you have any ideas, please discuss them with us in the comment section!
Related Blog